[Research highlight] Novel studies of CRISPR screening
CRISPR screening
Novel studies of CRISPR screening
CRISPR g ene editing technology has attracted the attention of many researchers due to its precise, simple, and efficient characteristics. In just a few years, it has become the most popular technology in the field of gene editing and is widely used in different biological fields. In this article, we shared the latest research trends in CRISPR library screening .
A pplication of CRISPR library screening technology in human pathogen research
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a common human pathogen, and its clinical treatment faces two challenges: drug resistance and the pathogenesis of Klebsiella pneumoniae . D ue to the lack of basic functional genomic data, there is limited research on the basic genetic mechanisms related to antimicrobial susceptibility.
In this study, a screening method for Klebsiella pneumoniae CRISPRi library , Mobile-CRISPRi-seq , was developed to identify genes that play key roles in in-vitro antibacterial adaptation and in - vivo host immunity. Mobile-CRISPRi-seq identified the deletion of folB and folP genes in the tetrahydrofolate synthesis pathway under trimethoprim screening for 870 CE genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae . They applied Mobile-CRISPRi-seq and comparative genomics screening strategies, and also identified genes waaE and fldA associated with susceptibility to polymyxin and β-lactam. In addition, multiple virulence genes were identified using a mouse infection model and Mobile-CRISPRi-seq. Among these genes, pal, yciS, and ribB were proven to be involved in the pathogenesis of Klebsiella pneumoniae . This study provides a simple, fast, and effective platform for screening potential antibacterial targets and virulence genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae . This CRISPR screening system can be extended to high-throughput functional gene research for various pathogenic bacteria, especially Gram negative bacteria.
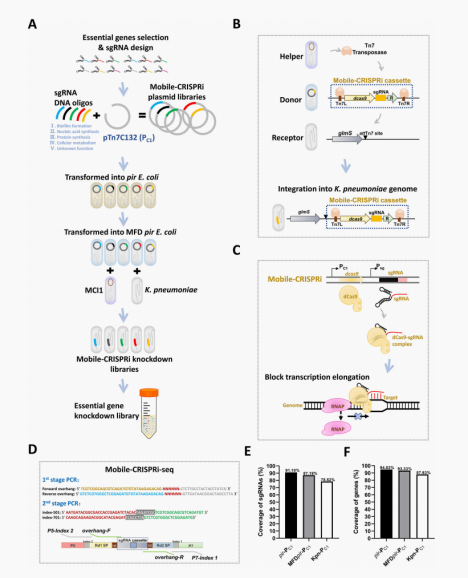
Construction of Mobile-CRISPRi Library of Klebsiella pneumoniae
CRISPRi library helps to study t he fine tuning mechanism of photosynthetic organisms
Blue-green algae bacteria are photosynthetic organisms that play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle and have been widely used in sustainable production of valuable chemicals. Therefore, understanding the role of blue-green algae genes is of great significance for guiding the application of all photosynthetic biotechnology.
This study used a CRISPR interference library for a blue-green algae model. PCC 6803 spans multiple light regions and carbon sources under the control of 11 bioreactors. This CRISPRi library targets 21705 individual mutants with high redundancy on all ORFs and ncRNAs. The extensive dataset has given importance to many previously unverified genes and proposed additional functions for central metabolic enzymes. Phosphate protein kinase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and small protein CP12 are crucial for mixed nutrition and photoheterotrophy, which means that in addition to the Calvin cycle in the dark, ternary complexes are also important for redirecting metabolic flux. In order to predict the efficacy of sgRNAs, machine analysis of sgRNA sequences and gene suppression data was performed, demonstrating the importance of proximal C enrichment and T deletion at the PAM site. This genes and regulatory mechanisms study under different conditions is of great significance for blue-green algae study.
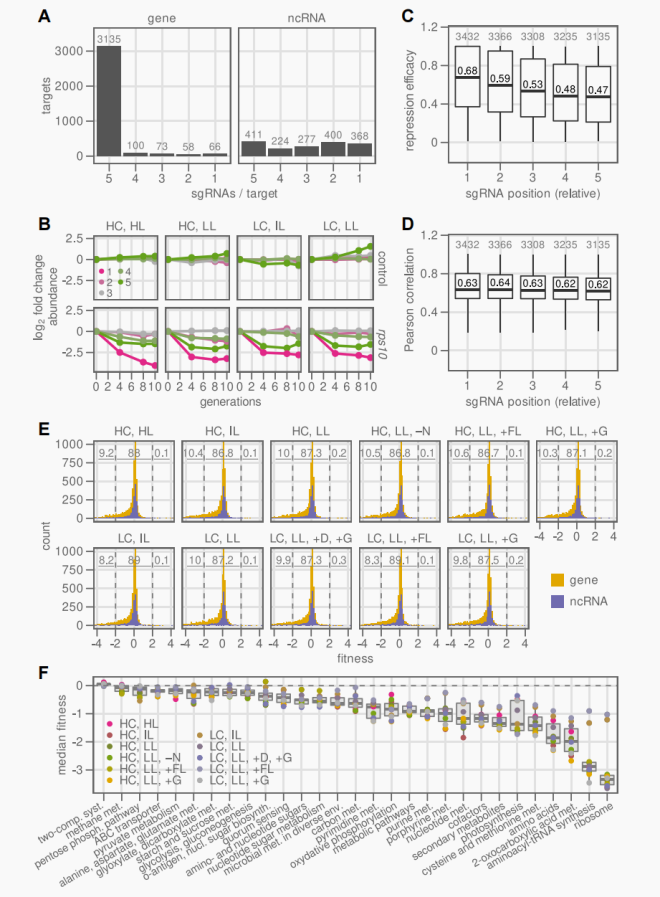
The CRISPRi library of Cymose algae targets most genes with 5 sgRNAs per gene. PCC6803 targets 3432 genes and 1 712 ncRNAs.
CRISPR library help optimize lentivirus vector
The lentivirus vector has become a powerful tool for treating hereditary and acquired human diseases. With the development of clinical research and commercial demand, the demand for a large number of purified lentivirus vectors is increasing .
This paper identifies genetic perturbations in human HEK293 cells and their derivatives by developing a CRISPR library screening method . This may increase s lentiviral vector titers. Simply put, lentivirus vectors based on CRISPRa and knockout libraries are used to modify HEK293 and HEK293T cells. The guiding RNAs (gRNAs) that may inhibit or enhance the production of lentiviral vectors were enriched and identified through next-generation sequencing (NGS). Although more work is needed to test the genes identified in this screening, the disturbance of the genes identified here is an antiviral innate immune inhibitor to generate cell lines that enhance the productivity of lentiviral vectors.
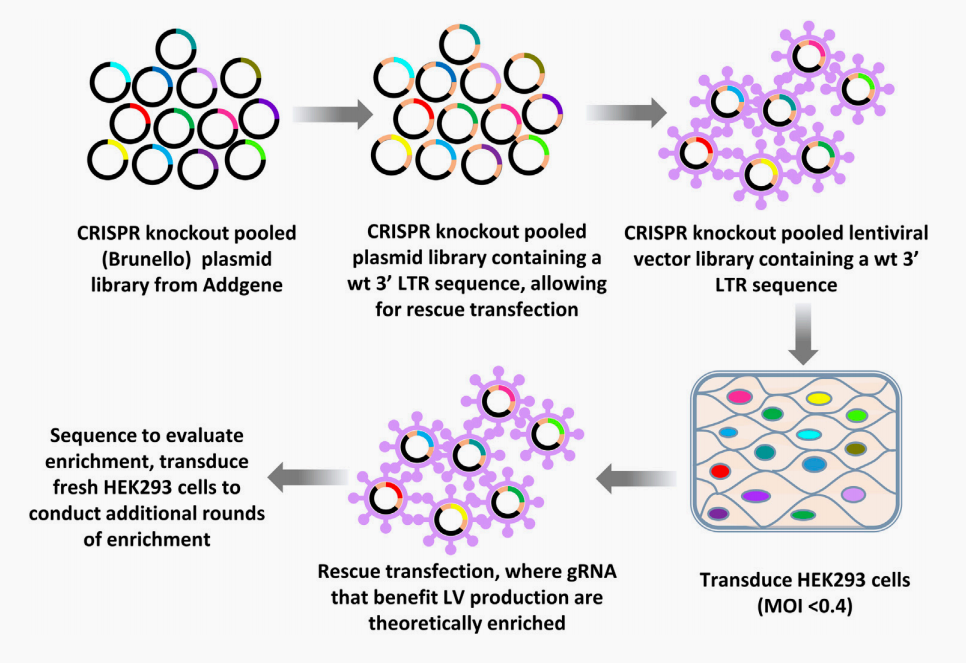
Workflow of determin ing gen es affects the production of lentivirus vectors by CRISPR knockout library screening
References
1. Construction and application of the conditionally essential gene knockdown library in Klebsiella pneumoniae to screen potential antimicrobial targets and virulence genes via Mobile-CRISPRiseq .
2. CRISPR interference screens reveal growth–robustness tradeoffs in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 across growth conditions .
3. CRISPR library screening to develop HEK293-derived cell lines with improved lentiviral vector titers .
1.EDITGENE provides various pre-made gene knockout library, lentiviral library only 1050 USD ! Check out our pre-made lentivirus libraries>>







![[Research highlight] Novel studies of CRISPR screening](/uploads/20241026/XHiPnuhZqGB0TM29_df01b08489a66591a81fdb641179f0f2.png)

Comment (4)