[Advanced Materials] Cas13 provides a new strategy for immunotherapy of tendon injuries
LwaCas13a

The study titled " Targeted Macrophage CRISPR-Cas13 mRNA Editing in Immunotherapy for Tendon Injury" published in Nature used LwaCas13a enzyme , which was provid ed by EDITGENE , to study the potential immunotherapy treatment.


This study not only provides new ideas for the application of CRISPR-Cas13 in tissue repair, but also offers new possibilities and prospects for the treatment of tendon injuries. By optimizing the delivery system and designing a ROS-responsive release mechanism, the team successfully achieved efficient editing of specific mRNAs in macrophages, which regulated macrophage function and promoted tendon tissue repair.
The research team constructed the Cas13 RNP complex , a core component of the CRISPR-Cas13 editing system. The complex recognizes and cleaves specific mRNAs to achieve gene editing.
2.Choos ing delivery systems for targeting macrophages
To efficiently deliver Cas13 RNP into macrophages, the team test ed a series of cationic polymers that have the ability to target macrophages. They found a delivery system that could efficiently introduce Cas13 RNP into macrophages.
3.Designing ROS r esponsive r elease m echanisms
During acute tendon injury, macrophages produce large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Taking advantage of this feature, the team designed a ROS-responsive release mechanism that enables Cas13 RNP to be released from the delivery system in response to ROS, thus enabling the editing of specific mRNAs in macrophages.
4.Modeling tendon injur y
To validate the effectiveness of the CRISPR-Cas13 editing system in tendon injury treatment, the team established a tendon injury model. They wrapped a composite membrane containing Cas13 RNP around the tendon injury site, enabling Cas13 RNP to directly contact and edit macrophages at the injury site.
During the experiment, the team regularly observed and recorded the healing of the tendon injury site, the activity of macrophages, and the expression level of SPP1 (encoded by OPN). The experimental results showed that by optimizing the delivery system of CRISPR-Cas13 and designing a ROS-responsive release mechanism, the research team successfully achieved efficient editing of specific mRNAs in macrophages. In the tendon injury model, Cas13 RNP was able to effectively inhibit the overexpression of SPP1, thereby attenuating macrophage activity and promoting tendon tissue repair. In addition, experiments also showed that the activation of fibroblasts and adhesion of surrounding tissues could be significantly reduced by wrapping the composite membrane containing Cas13 RNP around the tendon injury site, further confirming the effectiveness of the CRISPR-Cas13 editing system in the treatment of tendon injury.
The present study provides a new strategy for immunotherapy of tendon injury, i.e., RNA editing by the CRISPR-Cas13 system to regulate macrophage function in order to improve the tendon repair process. This provides new possibilities for future clinical applications and new ideas for repairing other types of tissue injuries.
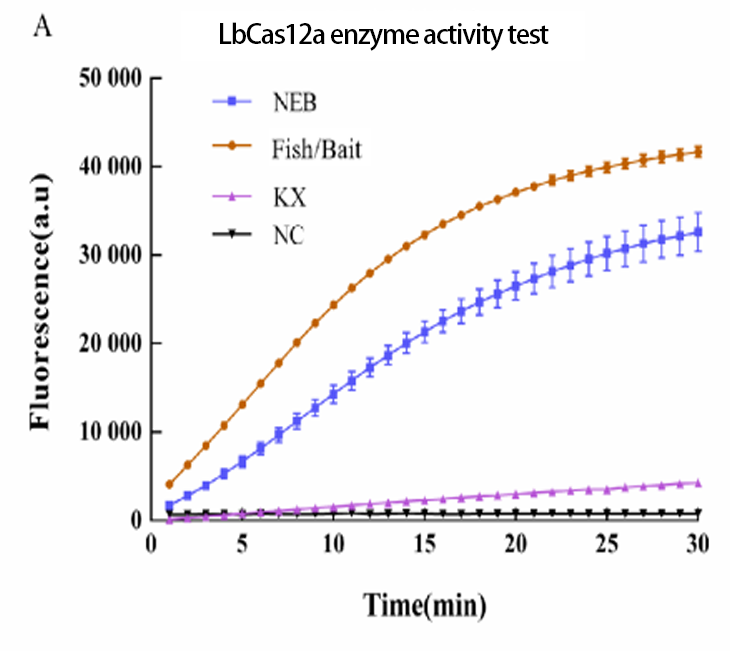
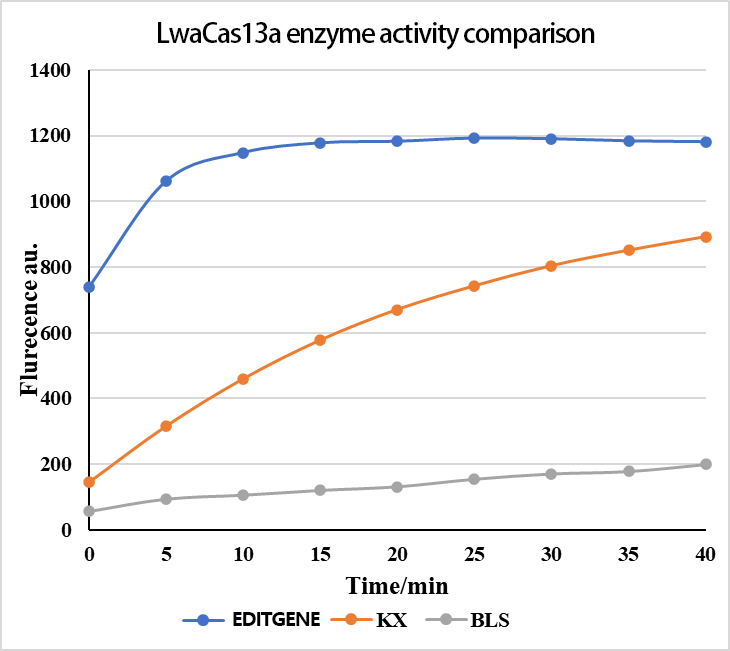
EDITGENE focuses on the utilization of CRISPR technology , independently develops a protein purification platform, providing high- activity Cas9 , Cas12 , Cas13 and other gene editing enzymes for scientific research .
Protein purification platform
EDITGENE's protein purification platform produces high purity and high activity Cas enzymes. The Cas enzymes are tested to have significant higher sensitivity than other brands in the market, and the detection limit can reach the amol level.
Recent Posts
[FEB Bestselling] CRISPR Screen for Metabolic, Transcription Factor, RNA-Binding Protein
[Research Frontier] New trends in CRISPR-- KO Cells Reveal Key Factors in Ferroptosis
[Nature] CRISPR Point Mutation Cells Help Deep Whole-genome Analysis
Contact Us








![[Advanced Materials] Cas13 provides a new strategy for immunotherapy of tendon injuries](/uploads/20241026/G7otXqng5J2R40hU_6b1e7d3bcc99e579649fc9f8f24ceae0.jpg)

Comment (4)